2 月 . 14, 2025 07:52
Back to list
polycarboxylic acid examples
Polycarboxylic acids represent a significant component in various industrial and consumer products. Their versatile nature allows them to be utilized in everything from textile treatments to concrete superplasticizers. This article delves into some noteworthy examples, highlighting their applications and importance.
Malonic Acid - Despite its niche presence, malonic acid is a critical intermediate in chemical synthesis, particularly in the production of barbiturates and other pharmaceuticals. Its role extends to stabilizing pH levels in electroplating processes, ensuring high-quality finishes on metal surfaces. As a buffer agent, its importance in maintaining biochemical reactions cannot be overstated. Adipic Acid - Predominantly known for its role in nylon production, adipic acid also finds use in food as a gelling agent and acidity regulator. Its ability to influence texture and consistency is leveraged in a plethora of dairy-based products, and it provides a unique tartness to jellies and jams that enhances flavor profiles. Glutamic Acid - In addition to its fame as a flavor enhancer in the form of monosodium glutamate (MSG), glutamic acid plays a pivotal role in food preservation. By adjusting acidity levels, it helps inhibit the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms, ensuring long shelf life for packaged goods. It's also gaining traction in biodegradable polymer production, furthering sustainability efforts. These examples highlight not only the diverse applications of polycarboxylic acids but also their critical role in advancing industrial processes and improving product quality. As industries continue to innovate, the demand for versatile chemical intermediates like polycarboxylic acids will undoubtedly grow. Their capacity to improve efficiency, sustainability, and consumer satisfaction makes them irreplaceable components in our daily lives and the backbone of many technological advancements. Their multifaceted usage across numerous sectors underpins their importance, continuously driving the need for research and development to explore future potential applications. This ongoing innovation positions polycarboxylic acids as vital contributors to modern industrial advancement, fostering a more sustainable and efficient future.

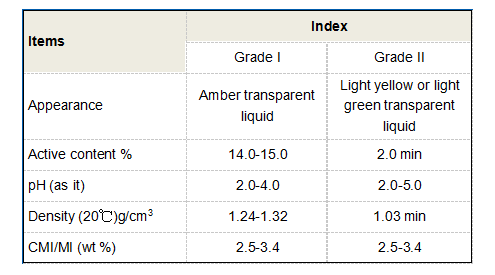
Malonic Acid - Despite its niche presence, malonic acid is a critical intermediate in chemical synthesis, particularly in the production of barbiturates and other pharmaceuticals. Its role extends to stabilizing pH levels in electroplating processes, ensuring high-quality finishes on metal surfaces. As a buffer agent, its importance in maintaining biochemical reactions cannot be overstated. Adipic Acid - Predominantly known for its role in nylon production, adipic acid also finds use in food as a gelling agent and acidity regulator. Its ability to influence texture and consistency is leveraged in a plethora of dairy-based products, and it provides a unique tartness to jellies and jams that enhances flavor profiles. Glutamic Acid - In addition to its fame as a flavor enhancer in the form of monosodium glutamate (MSG), glutamic acid plays a pivotal role in food preservation. By adjusting acidity levels, it helps inhibit the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms, ensuring long shelf life for packaged goods. It's also gaining traction in biodegradable polymer production, furthering sustainability efforts. These examples highlight not only the diverse applications of polycarboxylic acids but also their critical role in advancing industrial processes and improving product quality. As industries continue to innovate, the demand for versatile chemical intermediates like polycarboxylic acids will undoubtedly grow. Their capacity to improve efficiency, sustainability, and consumer satisfaction makes them irreplaceable components in our daily lives and the backbone of many technological advancements. Their multifaceted usage across numerous sectors underpins their importance, continuously driving the need for research and development to explore future potential applications. This ongoing innovation positions polycarboxylic acids as vital contributors to modern industrial advancement, fostering a more sustainable and efficient future.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





