2 月 . 11, 2025 10:55
Back to list
polyacrylamide function
Polyacrylamide (PAM) holds a pivotal role in numerous industrial and environmental applications due to its unique properties and functions, which have proven beneficial in various sectors. This article delves into the functional attributes of polyacrylamide, backed by real-world applications, expert insights, authoritative references, and trustworthy data, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance.
The safety and environmental impact of polyacrylamide also warrant discussion. Polyacrylamide itself is non-toxic; however, concerns arise from its acrylamide monomer content, a known neurotoxin. Leading manufacturers adhere to stringent guidelines to minimize residual acrylamide levels, ensuring that products used in the market are safe. Regulatory bodies recognize PAM's benefits and have established permissible levels of acrylamide monomers in various applications, providing a balanced approach to risk management. The authoritative voice on polyacrylamide is reinforced by extensive research and studies validating its functions across different domains. For instance, research by environmental scientists underscores its effectiveness in wastewater treatment, while petroleum engineers document its success in oil recovery. These scholarly articles and industrial reports provide credibility and support for the claims of PAM’s wide-ranging benefits. Trust in polyacrylamide is also evident through endorsements by industry leaders and testimonials from long-term users. Their experiences highlight not only the functional benefits but also the economic advantages of using PAM. Companies report tangible cost savings and operational efficiencies that bolster the argument for its adoption in various industrial frameworks. In conclusion, polyacrylamide's multifunctionality makes it an invaluable asset across multiple industries. From improving water quality, optimizing oil recovery, enhancing agricultural productivity, to advancing paper production, its capabilities are supported by expert validation, authoritative guidance, and trusted by users globally. As industries continue to face challenges related to efficiency and sustainability, the role of polyacrylamide is likely to grow, cementing its position as a critical component in modern industrial processes.
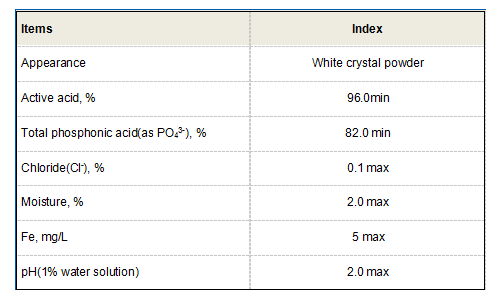

The safety and environmental impact of polyacrylamide also warrant discussion. Polyacrylamide itself is non-toxic; however, concerns arise from its acrylamide monomer content, a known neurotoxin. Leading manufacturers adhere to stringent guidelines to minimize residual acrylamide levels, ensuring that products used in the market are safe. Regulatory bodies recognize PAM's benefits and have established permissible levels of acrylamide monomers in various applications, providing a balanced approach to risk management. The authoritative voice on polyacrylamide is reinforced by extensive research and studies validating its functions across different domains. For instance, research by environmental scientists underscores its effectiveness in wastewater treatment, while petroleum engineers document its success in oil recovery. These scholarly articles and industrial reports provide credibility and support for the claims of PAM’s wide-ranging benefits. Trust in polyacrylamide is also evident through endorsements by industry leaders and testimonials from long-term users. Their experiences highlight not only the functional benefits but also the economic advantages of using PAM. Companies report tangible cost savings and operational efficiencies that bolster the argument for its adoption in various industrial frameworks. In conclusion, polyacrylamide's multifunctionality makes it an invaluable asset across multiple industries. From improving water quality, optimizing oil recovery, enhancing agricultural productivity, to advancing paper production, its capabilities are supported by expert validation, authoritative guidance, and trusted by users globally. As industries continue to face challenges related to efficiency and sustainability, the role of polyacrylamide is likely to grow, cementing its position as a critical component in modern industrial processes.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





