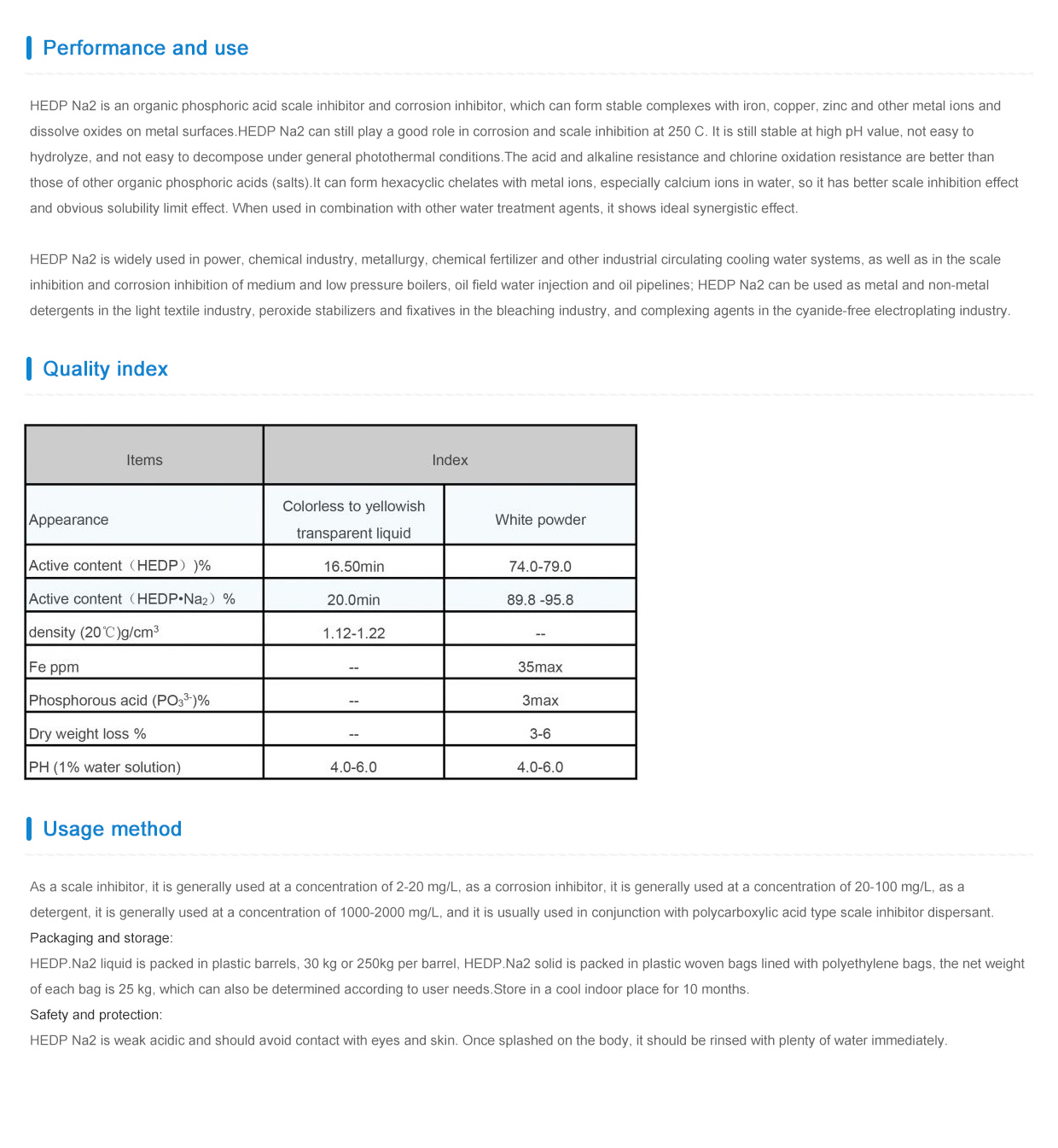
1 月 . 25, 2025 02:05
Back to list
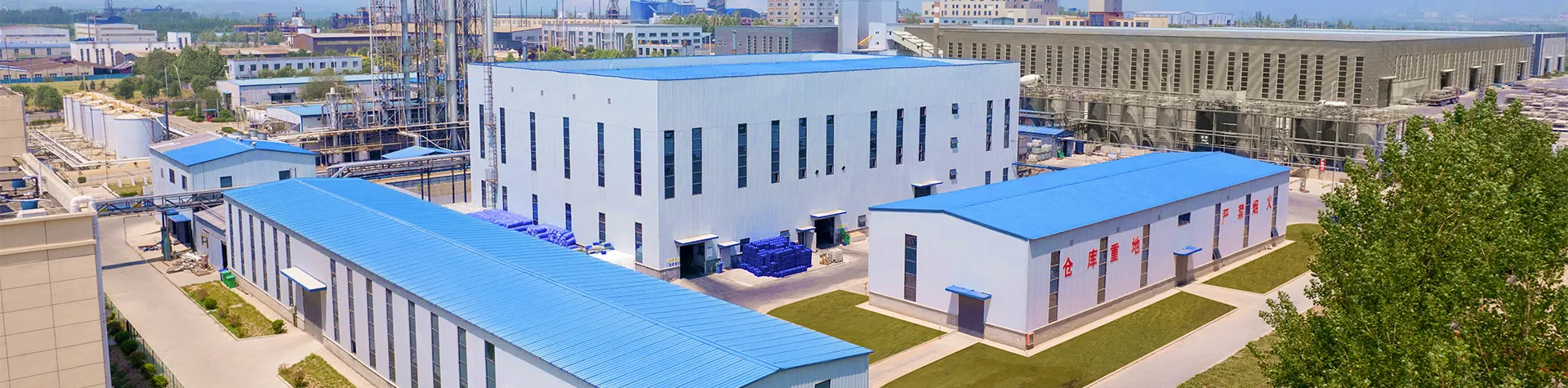
polyacrylamide factory
Polyacrylamide factories serve as critical hubs in the production of a versatile polymer that plays pivotal roles across various industries, ranging from water treatment to agriculture and mining. Drawing from years of involvement in the field, this guide delves into the complexities and importance of polyacrylamide manufacturing, providing insight into this indispensable industry.
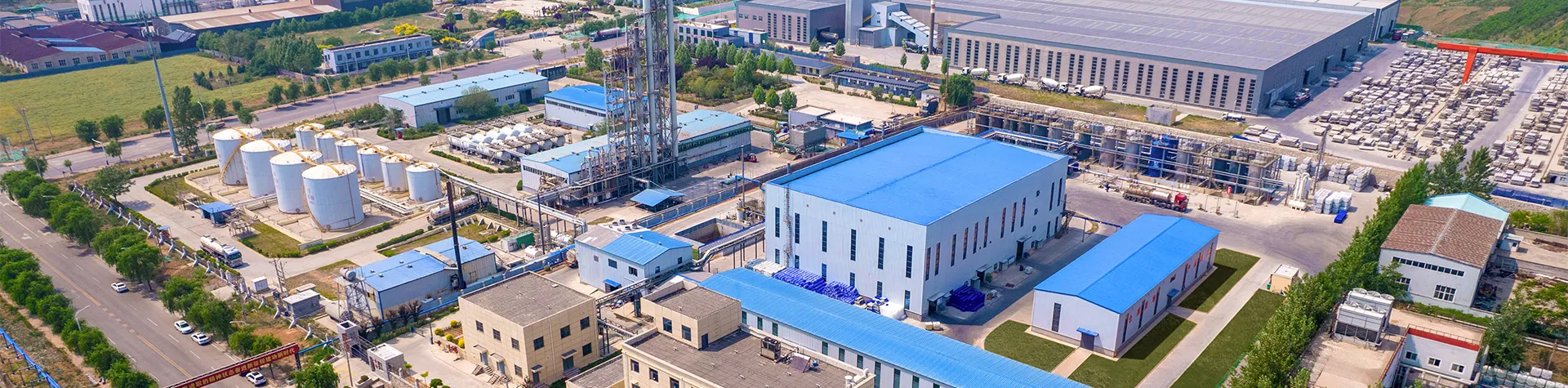
The authoritative stance of a factory is further consolidated by its global reach and partnerships. Collaborations with leading chemical companies and research institutions enable the exchange of knowledge and resources, propelling advancements in polyacrylamide applications and expanding its market presence. Real-world experiences serve to underline the importance of efficiency in a polyacrylamide production facility. From raw material procurement to final product delivery, each step requires a meticulous approach. For instance, selecting high-purity acrylamide not only enhances polymer quality but also reduces the potential for contamination, which can adversely affect product performance. Additionally, robust logistical networks contribute to the factory's credibility by ensuring timely distribution and minimizing supply chain disruptions. The ability to deliver polyacrylamide products on schedule is crucial for maintaining client trust and sustaining long-term business relationships. Ultimately, success in the polyacrylamide industry is measured by the factory's agility to adapt to market trends and technological innovations. Whether it's developing customized solutions for agricultural clients or improving oil recovery techniques, a proactive approach ensures industry leadership. In conclusion, the polyacrylamide factory represents a convergence of chemical expertise, operational efficiency, and innovative prowess. Upholding the principles of quality, sustainability, and reliability, these factories not only cater to the immediate needs of their clients but also contribute to future advancements in polymer applications. Through relentless dedication to excellence and a commitment to environmental stewardship, they secure their position as indispensable entities in the global industrial landscape.

The authoritative stance of a factory is further consolidated by its global reach and partnerships. Collaborations with leading chemical companies and research institutions enable the exchange of knowledge and resources, propelling advancements in polyacrylamide applications and expanding its market presence. Real-world experiences serve to underline the importance of efficiency in a polyacrylamide production facility. From raw material procurement to final product delivery, each step requires a meticulous approach. For instance, selecting high-purity acrylamide not only enhances polymer quality but also reduces the potential for contamination, which can adversely affect product performance. Additionally, robust logistical networks contribute to the factory's credibility by ensuring timely distribution and minimizing supply chain disruptions. The ability to deliver polyacrylamide products on schedule is crucial for maintaining client trust and sustaining long-term business relationships. Ultimately, success in the polyacrylamide industry is measured by the factory's agility to adapt to market trends and technological innovations. Whether it's developing customized solutions for agricultural clients or improving oil recovery techniques, a proactive approach ensures industry leadership. In conclusion, the polyacrylamide factory represents a convergence of chemical expertise, operational efficiency, and innovative prowess. Upholding the principles of quality, sustainability, and reliability, these factories not only cater to the immediate needs of their clients but also contribute to future advancements in polymer applications. Through relentless dedication to excellence and a commitment to environmental stewardship, they secure their position as indispensable entities in the global industrial landscape.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





