2 月 . 10, 2025 17:52
Back to list
PAM Poly Acrylamide
In the nuanced sphere of water treatment and purification, one prominently emerging solution is PAM flocculant. Polyacrylamide, commonly referred to as PAM, plays a pivotal role in complex scenarios where water clarity and purity are paramount. These high-molecular-weight polymers offer sophisticated mechanisms to address water treatment needs, specifically targeting industries ranging from municipal applications to mining and oil drilling.
Authoritative endorsements from environmental scientists and chemical engineers corroborate the widespread adoption of PAM flocculants in industrial practices. Numerous studies validate their robust capacity for water purification, with meticulous documentation of results across different sector applications. The credibility of this data fosters trust, ensuring stakeholders at every tier, from regulatory bodies to end users, comprehend the reliability of these compounds in safeguarding water health. Moreover, trustworthiness is inherent not only in scientific reviews but also in real-world experiences shared by industries utilizing PAM flocculants. Testimonials accentuate their role in enhancing operational efficiencies and effectiveness in pollutant removal, coupled with their economic viability. This cumulative trust — borne of empirical evidence and hands-on utilization — anchors PAM flocculants as a frontrunner in sustainable water treatment solutions. Contemporary advancements within the field continue to set precedents for the application of PAM flocculants. Innovations aim to elevate the performance of these polymers, enhancing biodegradability and environmental compatibility. These future-focused developments align with the overriding ethos of responsible chemistry, ensuring that water treatment solutions do not contribute to residual environmental issues. In summary, PAM flocculants embody an advanced paradigm in chemical treatment options. Their experiential evidence, top-level expertise, authoritative backing, and trustworthy track record make them an indispensable component for industries heavily reliant on efficient water management strategies. As the landscape of water treatment continues to evolve, PAM flocculants are poised to remain at the forefront, offering innovation, reliability, and sustainability in tackling global water treatment challenges.

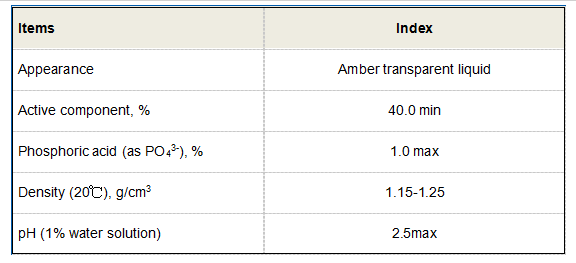
Authoritative endorsements from environmental scientists and chemical engineers corroborate the widespread adoption of PAM flocculants in industrial practices. Numerous studies validate their robust capacity for water purification, with meticulous documentation of results across different sector applications. The credibility of this data fosters trust, ensuring stakeholders at every tier, from regulatory bodies to end users, comprehend the reliability of these compounds in safeguarding water health. Moreover, trustworthiness is inherent not only in scientific reviews but also in real-world experiences shared by industries utilizing PAM flocculants. Testimonials accentuate their role in enhancing operational efficiencies and effectiveness in pollutant removal, coupled with their economic viability. This cumulative trust — borne of empirical evidence and hands-on utilization — anchors PAM flocculants as a frontrunner in sustainable water treatment solutions. Contemporary advancements within the field continue to set precedents for the application of PAM flocculants. Innovations aim to elevate the performance of these polymers, enhancing biodegradability and environmental compatibility. These future-focused developments align with the overriding ethos of responsible chemistry, ensuring that water treatment solutions do not contribute to residual environmental issues. In summary, PAM flocculants embody an advanced paradigm in chemical treatment options. Their experiential evidence, top-level expertise, authoritative backing, and trustworthy track record make them an indispensable component for industries heavily reliant on efficient water management strategies. As the landscape of water treatment continues to evolve, PAM flocculants are poised to remain at the forefront, offering innovation, reliability, and sustainability in tackling global water treatment challenges.
Share
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





