2 月 . 16, 2025 11:01
Back to list
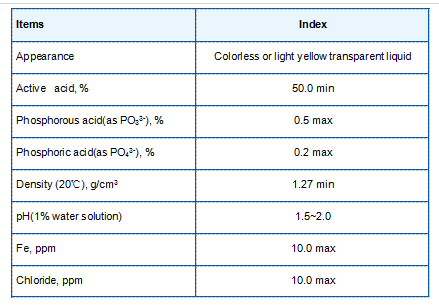
Tetra Sodium Salt of 1-Hydroxy Ethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid(HEDP·Na4)
The world of industrial water treatment is characterized by a continuous quest for efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Within this sphere, the role of chemical treatments, specifically Polyacrylamide (PAM), has been pivotal in enhancing water quality and process outcomes. From its inception, PAM has been utilized as a flocculant and coagulant in water treatment processes, owing to its unique ability to aggregate particles and impurities, allowing for their subsequent removal. However, beyond the traditional applications, this chemical's role continues to expand and evolve, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for environmentally conscious solutions.
To achieve optimal results, the dosing mechanism and integration with existing treatment systems must also be considered. Proper training for operating personnel is crucial, ensuring that PAM is applied correctly and safely, avoiding overdosing or underdosing which can lead to underperformance or unwanted residue in treated water. Partnering with chemical suppliers who offer robust support and technical guidance can further augment the effectiveness and reliability of PAM application. Moreover, the practice of continual monitoring and adjustment during treatment processes can prove beneficial in harnessing the full potential of PAM. Advances in sensor technology and automated systems offer unprecedented opportunities for real-time monitoring, allowing for immediate adjustments and more precise dosing. This not only improves treatment efficacy but also promotes resource conservation and operational cost reductions. Looking to the future, the role of PAM in water treatment is likely to evolve further with increased adoption of digital technology and data analytics. Predictive analytics, for instance, can provide valuable insights into treatment trends and potential system vulnerabilities, enabling proactive interventions and heightened control over water quality outcomes. The integration of such technological solutions with traditional chemical treatments epitomizes the direction of modern water management, where sustainability and technological innovation converge. On the radar of both consumers and regulatory bodies, issues of sustainability and environmental impact remain focal points. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprints and enhance resource efficiency, PAM stands out as a pivotal tool in achieving these ends. Nevertheless, the responsibility rests on industry leaders, policymakers, and researchers to ensure that its usage continually adapts to societal and ecological expectations. In conclusion, Polyacrylamide remains a cornerstone of chemical water treatment methodologies, distinguished by its adaptability and efficacy. In fostering cleaner environments and supporting industrial processes, its evolution is testament to the symbiotic relationship between scientific advancement and environmental stewardship. The journey of PAM, from basic coagulant to innovative environmental solution, underscores its indispensability in modern water management strategies. It is this blend of innovation, expertise, and commitment to sustainable practices that lays the groundwork for the future of water treatment.

To achieve optimal results, the dosing mechanism and integration with existing treatment systems must also be considered. Proper training for operating personnel is crucial, ensuring that PAM is applied correctly and safely, avoiding overdosing or underdosing which can lead to underperformance or unwanted residue in treated water. Partnering with chemical suppliers who offer robust support and technical guidance can further augment the effectiveness and reliability of PAM application. Moreover, the practice of continual monitoring and adjustment during treatment processes can prove beneficial in harnessing the full potential of PAM. Advances in sensor technology and automated systems offer unprecedented opportunities for real-time monitoring, allowing for immediate adjustments and more precise dosing. This not only improves treatment efficacy but also promotes resource conservation and operational cost reductions. Looking to the future, the role of PAM in water treatment is likely to evolve further with increased adoption of digital technology and data analytics. Predictive analytics, for instance, can provide valuable insights into treatment trends and potential system vulnerabilities, enabling proactive interventions and heightened control over water quality outcomes. The integration of such technological solutions with traditional chemical treatments epitomizes the direction of modern water management, where sustainability and technological innovation converge. On the radar of both consumers and regulatory bodies, issues of sustainability and environmental impact remain focal points. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprints and enhance resource efficiency, PAM stands out as a pivotal tool in achieving these ends. Nevertheless, the responsibility rests on industry leaders, policymakers, and researchers to ensure that its usage continually adapts to societal and ecological expectations. In conclusion, Polyacrylamide remains a cornerstone of chemical water treatment methodologies, distinguished by its adaptability and efficacy. In fostering cleaner environments and supporting industrial processes, its evolution is testament to the symbiotic relationship between scientific advancement and environmental stewardship. The journey of PAM, from basic coagulant to innovative environmental solution, underscores its indispensability in modern water management strategies. It is this blend of innovation, expertise, and commitment to sustainable practices that lays the groundwork for the future of water treatment.
Share
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





