organophosphonates
The Importance and Impact of Organophosphonates
Organophosphonates are a unique class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a phosphorus-to-carbon (P-C) bond. Unlike their more well-known cousins, the organophosphates, which contain phosphorus-to-oxygen (P-O) bonds, organophosphonates have garnered significant attention in both academic and industrial spheres due to their versatile applications and unique chemical properties. This article explores the structure, synthesis, applications, and environmental implications of organophosphonates.
Chemical Structure and Properties
The general chemical structure of organophosphonates can be represented as R-(C(P)(O)(OR')2), where R is a hydrocarbon group and R' are typically aliphatic or aromatic groups. The presence of the P-C bond imparts distinctive properties to organophosphonates, making them less toxic than organophosphates, which are often used in pesticides and can lead to severe health risks. One of the key attributes of organophosphonates is their stability; they exhibit a lower tendency to hydrolyze than organophosphates, which makes them useful in various applications requiring persistence.
Synthesis of Organophosphonates
The synthesis of organophosphonates is typically achieved through several methodologies. One of the most common approaches is the use of alkyl or aryl phosphonates with carbon nucleophiles under catalytic conditions. Another method involves the reaction of phosphonic acid derivatives with carbonyl compounds. Advances in synthetic techniques, including the development of greener chemistry practices, have also contributed to more efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis methods.
Applications of Organophosphonates
Organophosphonates have a wide array of applications across different fields
1. Agriculture While they are less toxic than organophosphates, organophosphonates still serve as effective agricultural agents. They can act as herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides, providing pest control while being relatively safer for non-target organisms.
organophosphonates
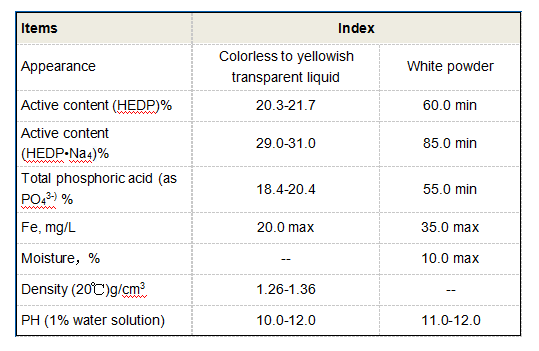
2. Chemical Warfare Certain organophosphonates have been investigated for their potential use in chemical warfare agents. Their stability and potency pose challenges for detection and decontamination, raising significant concerns regarding safety and security.
3. Pharmaceuticals In the pharmaceutical industry, organophosphonates are emerging as valuable compounds with potential applications in drug development. They can serve as building blocks for bioactive molecules, including antiviral and antitumor agents.
4. Materials Science Organophosphonates also play a role in materials science. They are used as additives in polymers, enhancing properties such as flame resistance and thermal stability. Given their ability to form stable films, they are also applied in coatings and surface treatments.
5. Environmental Chemistry In recent years, there has been increasing interest in the role of organophosphonates in environmental chemistry. They are investigated for their potential to serve as biodegradable alternatives to organophosphates, offering a more sustainable option for pest management while minimizing ecological impact.
Environmental Implications
While the advantages of organophosphonates are significant, their environmental implications must be closely monitored. The persistence and stability of these compounds raise concerns about their accumulation in ecosystems and potential toxicity to aquatic and terrestrial life. Research is ongoing to assess their environmental fate, transport, and interactions with various biological systems to better understand and mitigate any potential risks.
Furthermore, the development of analytical methods for the detection of organophosphonates in environmental samples is crucial. Techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry are being refined to enable trace-level detection, which can aid in monitoring their presence in water bodies, soil, and biota.
Conclusion
In summary, organophosphonates represent a significant class of compounds that bridge the fields of chemistry, agriculture, materials science, and environmental science. Their unique chemical characteristics confer a range of applications, promoting innovations that aim to enhance efficiency and safety in various sectors. However, as with any chemical compound, it is vital to evaluate their impact on health and the environment, ensuring that their use is guided by principles of sustainability and safety. The future of organophosphonates is bright, and ongoing research will surely uncover even more innovative uses and understanding of these versatile compounds.
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





