2 月 . 05, 2025 04:34
Back to list
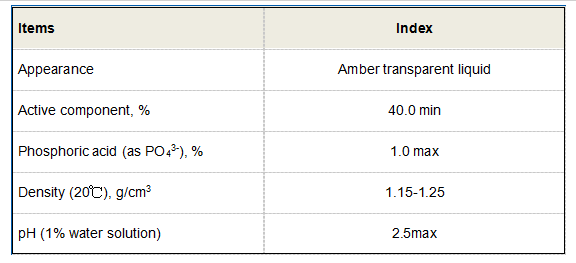
Disodium Salt of 1-Hydroxy Ethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid(HEDP•Na2)
Isothiazolinone-based preservatives have become a topic of significant discussion in recent years, particularly within the realm of consumer products. They are widely used in various industries, including cosmetics, household cleaning products, and industrial applications, due to their effectiveness in preventing microbial growth and ensuring product longevity. Understanding the impact and applications of these preservatives is crucial for manufacturers, regulators, and consumers alike.
Trustworthiness in the use of isothiazolinone-based preservatives hinges on transparency from manufacturers about their product formulations and potential risks. Brands that provide detailed ingredient lists and educate consumers on possible allergic reactions foster trust and improve consumer confidence. Additionally, third-party certifications and adherence to international standards serve as markers of reliability, assuring consumers of a product's safety profile. The product industry is continuously evolving, seeking to enhance the safety and efficacy of preservatives. Alternatives to isothiazolinones are under research, including natural antibacterial agents and synthetic compounds with reduced allergenic potential. Innovations in this sector are driven by both safety concerns and the push towards sustainable and environmentally friendly products. It is also crucial to consider the holistic aspect of product lifecycle assessment in incorporating isothiazolinones. Industry professionals are increasingly conscious of environmental impacts, from the sourcing of raw materials to the ultimate biodegradability of products. Potential pollution from production and disposal processes necessitates strategies for mitigating environmental footprints. In conclusion, isothiazolinone preservatives represent a delicate balance of technical expertise, regulatory compliance, and consumer safety considerations. As new research emerges and technology advances, the industry must adapt to maintain product safety without sacrificing efficacy. Enhanced education for both industry professionals and consumers, adherence to updated safety guidelines, and the pursuit of innovative solutions will ensure that these preservatives remain a viable option within the marketplace.

Trustworthiness in the use of isothiazolinone-based preservatives hinges on transparency from manufacturers about their product formulations and potential risks. Brands that provide detailed ingredient lists and educate consumers on possible allergic reactions foster trust and improve consumer confidence. Additionally, third-party certifications and adherence to international standards serve as markers of reliability, assuring consumers of a product's safety profile. The product industry is continuously evolving, seeking to enhance the safety and efficacy of preservatives. Alternatives to isothiazolinones are under research, including natural antibacterial agents and synthetic compounds with reduced allergenic potential. Innovations in this sector are driven by both safety concerns and the push towards sustainable and environmentally friendly products. It is also crucial to consider the holistic aspect of product lifecycle assessment in incorporating isothiazolinones. Industry professionals are increasingly conscious of environmental impacts, from the sourcing of raw materials to the ultimate biodegradability of products. Potential pollution from production and disposal processes necessitates strategies for mitigating environmental footprints. In conclusion, isothiazolinone preservatives represent a delicate balance of technical expertise, regulatory compliance, and consumer safety considerations. As new research emerges and technology advances, the industry must adapt to maintain product safety without sacrificing efficacy. Enhanced education for both industry professionals and consumers, adherence to updated safety guidelines, and the pursuit of innovative solutions will ensure that these preservatives remain a viable option within the marketplace.
Share
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





