3 月 . 07, 2025 03:19
Back to list
difference between flocculant and coagulant
Flocculants and coagulants are integral components within the water treatment industry, yet many still find the distinction between them somewhat perplexing. Their roles, while interconnected, have distinct properties and applications that are critical for effective water treatment. For industry professionals, understanding these differences is essential not just for enhancing performance but also for optimizing cost efficiency and achieving sustainability goals.
Authoritative voices within the sector advocate for a holistic approach to water treatment wherein the intertwining roles of flocculants and coagulants are optimized through real-time monitoring and automated dosing systems. Such technology reduces human error, adapts to fluctuating water quality, and minimizes chemical use—aligning economic efficiency with environmental stewardship. An example illustrating the critical difference between coagulants and flocculants can be found in the treatment of industrial effluents. Industries like textile dyeing, which generate wastewater rich in suspended solids and organic colors, typically rely heavily on coagulants to address color removal goals. Coagulants act swiftly to neutralize charge, and this is often followed by a judicious selection of flocculants to achieve a visual clarity that surpasses regulatory thresholds. Trustworthiness in the industry stems from transparency around product specifications, sourcing, and usage impacts. Professionals working with these chemicals are expected to maintain rigorous safety and environmental standards, reflected in Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and compliance with bodies such as the EPA or local water authorities. Trust also extends to lab-scale trials that verify vendor claims on product effectiveness and adaptability to specific conditions. Given the escalating challenges in global water scarcity and pollution, innovative developments continue to emerge in the realm of flocculation and coagulation. Renewable and biodegradable options are already gaining traction. Such innovations not only address ecological responsibilities but also future-proof operations against evolving regulations and shortages in traditional raw materials. The difference between flocculants and coagulants may appear subtle; however, those differences are at the crux of advanced water treatment processes. By leveraging a strategic understanding of these agents’ integral roles, backed by experience, expertise, and continual technological innovation, industries can achieve superior water quality, lower operational costs, and fulfill their environmental commitments.
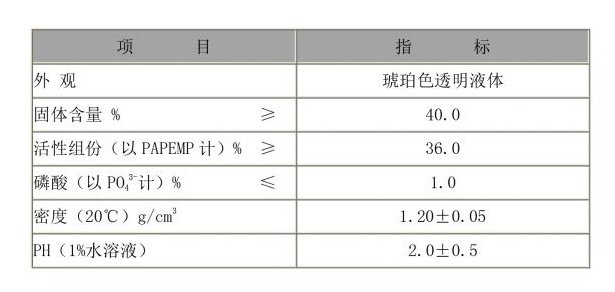

Authoritative voices within the sector advocate for a holistic approach to water treatment wherein the intertwining roles of flocculants and coagulants are optimized through real-time monitoring and automated dosing systems. Such technology reduces human error, adapts to fluctuating water quality, and minimizes chemical use—aligning economic efficiency with environmental stewardship. An example illustrating the critical difference between coagulants and flocculants can be found in the treatment of industrial effluents. Industries like textile dyeing, which generate wastewater rich in suspended solids and organic colors, typically rely heavily on coagulants to address color removal goals. Coagulants act swiftly to neutralize charge, and this is often followed by a judicious selection of flocculants to achieve a visual clarity that surpasses regulatory thresholds. Trustworthiness in the industry stems from transparency around product specifications, sourcing, and usage impacts. Professionals working with these chemicals are expected to maintain rigorous safety and environmental standards, reflected in Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and compliance with bodies such as the EPA or local water authorities. Trust also extends to lab-scale trials that verify vendor claims on product effectiveness and adaptability to specific conditions. Given the escalating challenges in global water scarcity and pollution, innovative developments continue to emerge in the realm of flocculation and coagulation. Renewable and biodegradable options are already gaining traction. Such innovations not only address ecological responsibilities but also future-proof operations against evolving regulations and shortages in traditional raw materials. The difference between flocculants and coagulants may appear subtle; however, those differences are at the crux of advanced water treatment processes. By leveraging a strategic understanding of these agents’ integral roles, backed by experience, expertise, and continual technological innovation, industries can achieve superior water quality, lower operational costs, and fulfill their environmental commitments.
Share
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





