2 月 . 15, 2025 03:06
Back to list
cas number 2682 20 4
Chemical compound enthusiasts and professionals frequently encounter CAS number 2682-20-4, pointing to an essential preservative widely researched and used across multiple industries. This compound, known as 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (MIT), plays a pivotal role in preserving personal care products, paints, and household cleaners due to its potent antimicrobial properties.
The scientific community's continuous research into MIT's efficacy and safety underscores the ongoing efforts to optimize its use. Studies focus on enhancing its stability and effectiveness, ensuring that it remains an indispensable player in formulations requiring preservative action. These developments highlight MIT's enduring relevance and adaptability to situationally evolving product safety and regulatory landscapes. In the context of sustainability, MIT is viewed as a favorable option due to its relatively low concentrations needed to achieve antimicrobial effects, thereby reducing ecological footprint compared to some alternatives. Its inclusion in formulations also means a reduction in waste due to product spoilage, aligning with global sustainability goals to create and maintain eco-friendly industrial practices. As the chemical industry evolves, embracing safer and more sustainable preservation methods will be paramount. Innovations centered around MIT utilization continue to emerge, reflecting its adaptability and enduring significance. Manufacturers devoted to safety, quality, and sustainability find MIT indispensable, ensuring they meet both consumer expectations and regulatory demands. Across industries, MIT remains a testament to the balance between nature and technology, illustrating how tailored chemical solutions can address contemporary industrial challenges. Its efficacy, backed by authoritative research and regulatory compliance, ensures its position as a reliable preservative while encouraging a commitment to safe and sustainable consumption.
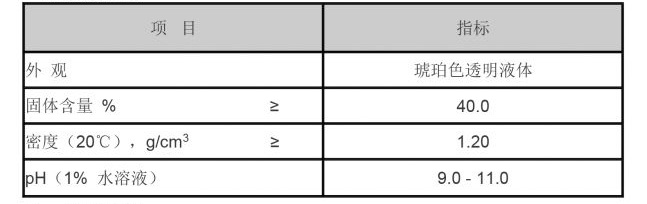
The scientific community's continuous research into MIT's efficacy and safety underscores the ongoing efforts to optimize its use. Studies focus on enhancing its stability and effectiveness, ensuring that it remains an indispensable player in formulations requiring preservative action. These developments highlight MIT's enduring relevance and adaptability to situationally evolving product safety and regulatory landscapes. In the context of sustainability, MIT is viewed as a favorable option due to its relatively low concentrations needed to achieve antimicrobial effects, thereby reducing ecological footprint compared to some alternatives. Its inclusion in formulations also means a reduction in waste due to product spoilage, aligning with global sustainability goals to create and maintain eco-friendly industrial practices. As the chemical industry evolves, embracing safer and more sustainable preservation methods will be paramount. Innovations centered around MIT utilization continue to emerge, reflecting its adaptability and enduring significance. Manufacturers devoted to safety, quality, and sustainability find MIT indispensable, ensuring they meet both consumer expectations and regulatory demands. Across industries, MIT remains a testament to the balance between nature and technology, illustrating how tailored chemical solutions can address contemporary industrial challenges. Its efficacy, backed by authoritative research and regulatory compliance, ensures its position as a reliable preservative while encouraging a commitment to safe and sustainable consumption.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





