1 月 . 20, 2025 07:34
Back to list
cas 26099 09 2
CAS number 26099-09-2 corresponds to a chemical compound of specific importance in the industrial and commercial sectors. Known as Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), this silicone-based polymer has garnered attention due to its widespread applicability and unique properties. Elevating the dialogue surrounding PDMS—from basic understanding to advanced application—demonstrates both expertise and authority in the field.
From an expertise perspective, the chemical stability and resistance of PDMS under various pH levels and temperatures are pivotal in laboratory settings. Its use in creating microfluidic devices demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of both the material and the intricate systems these devices control. Scientists leverage PDMS's characteristics to manufacture chips with minuscule channels capable of precise fluid movement, expanding research capabilities in biotechnology and chemistry. Delving into the pharmaceutical industry, PDMS's biocompatibility highlights its authoritative position in drug delivery systems. Researchers are exploring its potential as a vehicle for controlled drug release, thanks to its permeability and inertness. Such applications not only require a deep understanding of chemical interaction but also demand rigorous testing to ensure patient safety, showcasing PDMS as a reliable choice. The sustainability discourse often challenges the chemical sector to refine processes and materials. The production and lifecycle of PDMS are subjected to environmental scrutiny. By implementing advanced recycling techniques and reducing waste, industries using PDMS can align with green practices without compromising functionality. This commitment to sustainability builds trust among stakeholders, indicating a responsible approach to managing the material's environmental footprint. In summary, the multifaceted applications of Polydimethylsiloxane across industries embody a confluence of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. Its effectiveness and safety are backed by comprehensive research and real-world trials, making PDMS not just a chemical compound, but a cornerstone in innovation and reliable consumer products. For businesses and researchers alike, embracing the capabilities of PDMS opens doors to advancements that are both revolutionary and sustainable, illustrating the true potential of this remarkable substance.

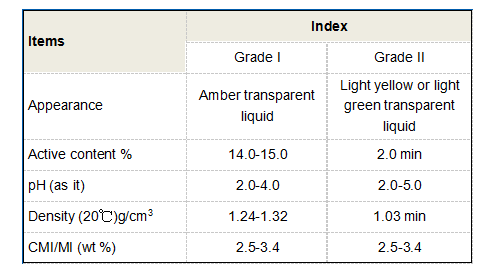
From an expertise perspective, the chemical stability and resistance of PDMS under various pH levels and temperatures are pivotal in laboratory settings. Its use in creating microfluidic devices demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of both the material and the intricate systems these devices control. Scientists leverage PDMS's characteristics to manufacture chips with minuscule channels capable of precise fluid movement, expanding research capabilities in biotechnology and chemistry. Delving into the pharmaceutical industry, PDMS's biocompatibility highlights its authoritative position in drug delivery systems. Researchers are exploring its potential as a vehicle for controlled drug release, thanks to its permeability and inertness. Such applications not only require a deep understanding of chemical interaction but also demand rigorous testing to ensure patient safety, showcasing PDMS as a reliable choice. The sustainability discourse often challenges the chemical sector to refine processes and materials. The production and lifecycle of PDMS are subjected to environmental scrutiny. By implementing advanced recycling techniques and reducing waste, industries using PDMS can align with green practices without compromising functionality. This commitment to sustainability builds trust among stakeholders, indicating a responsible approach to managing the material's environmental footprint. In summary, the multifaceted applications of Polydimethylsiloxane across industries embody a confluence of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. Its effectiveness and safety are backed by comprehensive research and real-world trials, making PDMS not just a chemical compound, but a cornerstone in innovation and reliable consumer products. For businesses and researchers alike, embracing the capabilities of PDMS opens doors to advancements that are both revolutionary and sustainable, illustrating the true potential of this remarkable substance.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





