2 月 . 12, 2025 21:54
Back to list
butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
In the ever-evolving realm of specialty chemicals, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid emerges as a compound of significant interest, both for its chemical properties and its potential applications across various industries. As industry professionals and researchers seek innovative solutions, understanding the nuances of this compound's applications, synthesis, and benefits can yield substantial advantages.
From a synthesis perspective, the methods used to produce butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid are equally pivotal. Advanced synthetic protocols that incorporate green chemistry principles are gaining traction. These approaches not only minimize environmental impact but also ensure the production process remains cost-effective and efficient. Researchers are continually exploring novel catalysts and reaction conditions that further improve yield and purify this compound, painting a promising picture for future applications. Industry experts acknowledge the potential of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid in materials science, particularly in the creation of novel polymers and resins. Its incorporation in polymeric matrices can enhance material properties such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to degradation. Such innovations pave the way for new materials that could revolutionize sectors such as construction, automotive, and electronics, providing manufacturers with the tools to develop high-performance, durable products. As a trusted entity in the specialty chemicals market, understanding the regulatory landscape around the use of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is paramount. Ensuring compliance with industry standards and environmental regulations serves not only to protect public health but also to bolster the credibility of companies utilizing this compound in their products. Transparency in sourcing and manufacturing processes further instills trust among consumers and industry stakeholders, reinforcing the compound's reputation as a viable and reliable ingredient. For businesses looking to integrate butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid into their product lines, collaboration with experts in chemical engineering and formulation can yield substantial benefits. Such collaboration ensures that the compound's unique attributes are leveraged effectively, enhancing product quality and market competitiveness. By staying abreast of ongoing research and technological advancements, companies can harness the full potential of this versatile chemical to drive innovation and meet evolving market demands.

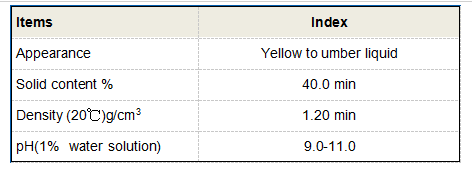
From a synthesis perspective, the methods used to produce butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid are equally pivotal. Advanced synthetic protocols that incorporate green chemistry principles are gaining traction. These approaches not only minimize environmental impact but also ensure the production process remains cost-effective and efficient. Researchers are continually exploring novel catalysts and reaction conditions that further improve yield and purify this compound, painting a promising picture for future applications. Industry experts acknowledge the potential of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid in materials science, particularly in the creation of novel polymers and resins. Its incorporation in polymeric matrices can enhance material properties such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to degradation. Such innovations pave the way for new materials that could revolutionize sectors such as construction, automotive, and electronics, providing manufacturers with the tools to develop high-performance, durable products. As a trusted entity in the specialty chemicals market, understanding the regulatory landscape around the use of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid is paramount. Ensuring compliance with industry standards and environmental regulations serves not only to protect public health but also to bolster the credibility of companies utilizing this compound in their products. Transparency in sourcing and manufacturing processes further instills trust among consumers and industry stakeholders, reinforcing the compound's reputation as a viable and reliable ingredient. For businesses looking to integrate butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid into their product lines, collaboration with experts in chemical engineering and formulation can yield substantial benefits. Such collaboration ensures that the compound's unique attributes are leveraged effectively, enhancing product quality and market competitiveness. By staying abreast of ongoing research and technological advancements, companies can harness the full potential of this versatile chemical to drive innovation and meet evolving market demands.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Ultimate Guide to Flocculants: Transforming Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Improve Your Water Treatment Solutions with PolyacrylamideNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024
-
Empower You to Achieve the Highest Standards of Water QualityNewsNov.01,2024
-
Effective Scale InhibitorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Discover the Power of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water TreatmentNewsNov.01,2024





